This is not the first time BS7799 has been proposed as an ISO standard. The original version, BS7799:1995 was submitted in the summer of 1996 but was narrowly defeated. Those countries who voted in its favor were not dismayed, however. Australia and New Zealand for example recast it (by changing the UK legislative references to corresponding Australian and New Zealand references) and re-published it as AS/NZS 4444. The Netherlands embraced it wholesale and established a certification scheme, which went live early 1997. This international interest encouraged the British to develop the standard further. BS7799, How it works? Please note that ISO/IEC 17799:2005 just been published (15 June 2005). It replaces ISO/IEC 17799:2000. This means that Annex A of the current ISMS standard (BS7799-2:2002) is now out of date, as it refers to ISO/IEC 17799:2000. There will be an ISO/IEC version of BS7799-2:2002. It is anticipated that this will be published early next year and will be called ISO/IEC 27001. The Management Standard BS7799-2:2002 instructs you how to apply ISO/IEC 17799 and how to build, operate, maintain and improve an ISMS. The 1999 edition only instructed you to apply ISO/IEC 17799 and build an ISMS. The major components of an ISMS are summarized in Figure 1. The activities continually cycle around the PLAN-DO-CHECK-ACT cycle.
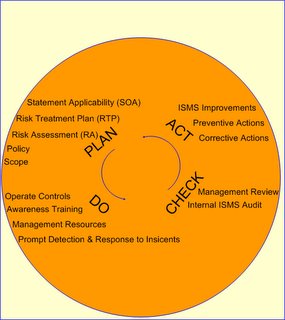
Figure1
The Code of Practice
ISO/IEC 17799:2005 defines 132 security controls structured under 11 major headings as follows:
- Security Policy
- Organizing Security
- Asset Management
- Human Resource Management
- Physical and Environmental Security
- Communication and Operation Management
- Access Control
- Information System Acquisition, development and maintenance
- Information Security Incident Management
- Business Continuity Management
- Compliance
These enable readers to identify the particular safeguards that are appropriate to their particular business or specific area of responsibility.
ISMS Standards Overview
The scope of any ISMS includes
1. People
2. Processes
3. IT systems
4. Policies
Concerns
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
BS7799-2:2002 is a management standard, and explains how to build, maintain and improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It is predicated on risk assessment and the Plan-Do-Check-Act model, which are two vital ingredients of corporate governance. Thus, BS7799-2:2002 provides an excellent basis on which to build the management controls necessary to achieve an organization’s mission, to manage risk, to assure effective control and to seek improvements where appropriate. ISMS forms a part of an organization’s internal control system. The 7799 standards are particularly pertinent to corporate governance in an "e-biz" context, where risk management not only has to contend with the usual risks of doing business but also with rapidly changing IT/Internet risks and multiple legal jurisdictions. Thus the standards explain how to address the all-to-common and often devastating business impacts caused by viruses, web-site outages, improper disclosure of customer account details and incorrect pricing information. A growing number of politicians and leaders of industry are now recognizing the importance of these standards. Businesses, notably throughout Europe and Asia, who have a desire to flourish in the Information Age, are already taking advantage of ISO/IEC 17799.
Document and Data Control Procedure
- Information Security Manual
- Asset List/Risk Management Plan
- Statement of Applicability
- Guidelines
- Templates and Formats.
Goals of ISMS
Define and implement process and policies that protect our business assets and ensures efficient business operations and business continuity. Track and keep space with changing requirement of business and threat scenarios. Meet statutory requirements and implement security solution that are cost effective and that afford ease of use for meeting our information goal.
Security Policy
- Protect confidentiality, Integrity and availability of our business
- Meet contractual obligations on information security
- Meet regulatory and legislation requirements
- Ensure business continuity
- Undertake proactive actions and implement relevant information security policies to prevent security breaches
FAQ
1.What is ISMS ?
Information Security Management System, it mainly deals with protecting business assets.
What are business Assets ?
- Information. Database, System Documents, training materia, so on.
- Software. Developed and bought.
- Documents. Hard copy & softcopy, viz. Contracts, manuals, so on.
- People. Employees.
- Services – UPS, Power, so on
- Company Image and Reputation
What are the three concern properties of ISMS?
- Confidentiality. Ensuring that information is accessible to authorized access.
- Integrity. Safe guard the accuracy and completeness of information.
- Availability. Ensuring that authorized users have access to information.
Do you have internal audit?
Yes we have it once in every quarter
How is the audit conducted?
It is conducted by the Information Security officer. They investigate and recommend corrective ness/Preventive actions according to ISMS norms and close the same when they are resolved.
How do you protect sensitive data?
Any information that is considered sensitive will be password protected.
What is password policy?
- Every employee has to secure his password strictly, do not reveal it even to family member while working at home.
- Should not reveal it even to the CEO of the company.
- Password changes after every 45 days.
- Min length of password is of 8 Characters, with a combination of upper case, lower case and punctuation characters as well as letters.
- Should not have names like family members, pets, friends, coworkers, fantasy characters, computer terms, birth day.
What policies should not be violated?
- Copy Rights
- Trade secret
- Patents or Intellectual Properties
- Inappropriate licenses
Can we provide information to others outside company?
No, we should not provide information to other parties outside company.
What will you do when you find some sensitive documents in the office premises or some body violating the rules?
Inform it to the BCP (Business Continuity Plan) representatives of that month.
Are you permitted to bring outside material in the office premises?
No, you are not permitted to bring inside the office, we leave it at the security guard.
What will you do when fire breaks or there is an earth quack?
Don't panic; take proper steps to avoid calamities. Prepare yourself through mock-up drill.
What will you do when virus attacks your system?
We will first remove the network cable or shutdown the system and inform to the network administrator.
What is your asset Manager?
We maintain all the information in the VSS (Virtual Storage System) and access to VSS is given according to the need of the user.
What is HIPAA?
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Information should be protected as it deals with Health based information.
Were you given an induction, when you joined the company?
Yes.
1 comment:
I actually enjoyed reading through this posting. Many thanks.We are a managed security service provider in Bangalore that provides a variety of consulting and managed security engagements. Our outsourced solutions to assist manage your organization's security needs. Security service provider in Bangalore
Post a Comment